Značaj kombinovane primene elektrofizioloških ispitivanja i ispitivanja magnetne rezonance brahijalnog pleksusa za potvrdu dijagnoze multifokalne motorne neuropatije
Sažetak
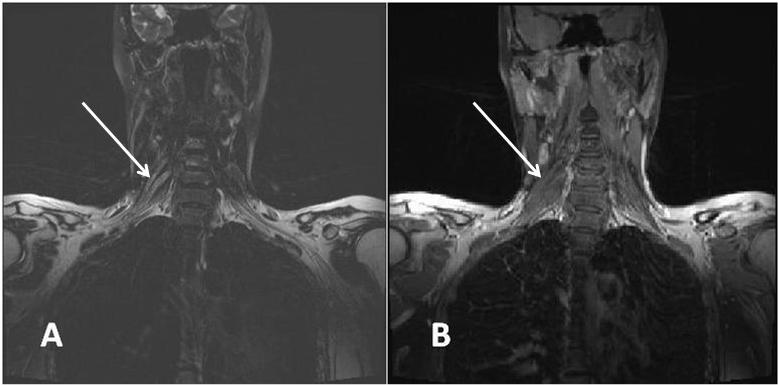
Uvod/Cilj. Multifokalna motorna neuropatija (MMN) je imunski posredovano oboljenje perifenih nerava koje karakteriše sporo napredovanje asimetričnih slabosti mišića ekstremiteta, bez poremećaja senzibiliteta. Cilj rada bio je da se ispita značaj kombinovane primene magnetne stimulacije u cervikalnom nivou i magnetne rezonance (MR) brahijalnog pleksusa u potvrdi proksimalnih blokova provođenja kod obolelih od MMN. Takođe, želeli smo da utvrdimo da li postoje znaci oštećenja nervnih korenova koji grade nerve koji inervišu klinički slabe mišiće, kod kojih konvencionalnim ispitivanjem provodljivosti perifernih nerava nije registrovano postojanje blokova provođenja (BP). Metode. U studiju je bilo uključeno devet bolesnika sa klinički i elektrofiziološki potvrđenom dijagnozom MMN. Svim bolesnicima urađen je MR vratnog dela kičme i brahijalnog pleksusa u T1 i turbo spin-eho T1 sekvenci, aksijalnoj turbo spin-eho T2 sekvenci i koronarnoj turbo spin-eho T2 sekvenci sa saturacijom masti, pomoću aparata Simens Avanto jačine 1.5 T. Rezultati. Kod svih bolesnika registrovana je izražena asimetrična distalna slabost mišića inervisanih radijalnim, ulnarnim, medijalnim i peronealnim nervima, sa najupečatljivijom kliničkom prezentacijom viseće šake i prstiju. Analizom cerebrospinalnog likvora zabeležena je blaga proteinorahija kod većine obolelih. U serumu šest bolesnika nađena su poliklonska anti-GM1 antitela. Elektromioneurografija (EMG) pokazala je znake neurogene lezije, predominantno u distalnoj muskulaturi inervisanoj radijalnim nervom. Kod svih bolesnika registrovan je parcijalni BP van uobičajenih mesta kompresije radijalnog, ulnarnog, medijalnog i peronealnog nerva, a MR pregledom detektovane su zone pojačanog intenziteta signala u najmanje jednom cervikalnom korenu, trunkusu ili fascikulusu brahijalnog pleksusa. Kod tri bolesnika kod kojih standardnim elektroneurografskim pregledom nije registrovano postojanje BP primenom magnetne stimulacije u cervikalnom nivou sugerisani su proksimalni BP, što je bilo u korelaciji sa MR promenama odgovarajućih cervikalnih korenova. Zaključak. Rezultati ispitivanja pokazuju korelaciju između mišićne slabosti, produženog vremena provođenja kroz motorne korenove i promena na MR brahijalnog pleksusa, što je od posebnog značaja za nerve koji inervišu klinički slabe mišiće, a kod kojih primenom konvencionalne elektroneurografije nije moguće detektovati BP.
Reference
Parry GJ, Sumner AJ. Multifocal motor neuropathy. Neurol Clin 1992; 10(3): 671−84.
Nobile-Orazio E, Cappellari A, Priori A. Multifocal motor neuro-pathy: Current concepts and controversies. Muscle Nerve 2005; 31(6): 663−80.
Slee M, Selvan A, Donaghy M. Multifocal motor neuropathy: the diagnostic spectrum and response to treatment. Neurology 2007; 69(17): 1680−7.
Olney RK. Consensus criteria for the diagnosis of partial con-duction block. Muscle Nerve 1999; 22(8): 225−9.
Arunachalam R, Osei-Lah A, Mills KR. Transcutaneous cervical root stimulation in the diagnosis of multifocal motor neuropa-thy with conduction block. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 2003; 74(9): 1329−31.
van Es HW, Van BLH, Franssen H, Witkamp TD, Ramos LM, Notermans NC, Wokke JH. Magnetic resonance imaging of the brachial plexus in patients with multifocal motor neuropathy. Neurology 1997; 48(5): 1218−24.
Cats EA, Jacobs BC, Yuki N, Tio-Gillen AP, Piepers S, Franssen H, et al. Multifocal motor neuropathy: association of anti-GM1 IgM antibodies with clinical features. Neurology 2010; 75(22): 1961−7.
van Schaik IN, Bouche P, Illa I, Léger JM, van den Bergh P, Cornblath DR, et al. European Federation of Neurological So-cieties/Peripheral Nerve Society guideline on management of multifocal motor neuropathy. Eur J Neurol 2006; 13(8): 802−8.
Meuth SG, Kleinschnitz C. Multifocal motor neuropathy: update on clinical characteristics, pathophysiological concepts and therapeutic options. Eur Neurol 2010; 63(4): 193−204.
Joint Task Force of the EFNS and the PNS. European Feder-ation of Neurological Societies/Peripheral Nerve Society Guideline on management of multifocal motor neuropathy. Report of a Joint Task Force of the European Federation of Neurological Societies and the Peripheral Nerve Society - first . J Peripher Nerv Syst 2010; 15(4) 295−301.
Inaba A, Yokota T, Otagiri A, Nishimura T, Saito Y, Ichikawa T, et al. Electrophysiological evaluation of conduction in the most proximal motor root segment. Muscle Nerve 2002; 25(4): 608−11.
Taylor BV, Gross L, Windebank AJ. The sensitivity and specificity of anti-GM1 antibody testing. Neurology 1996; 47(4): 951−5.
Poceva-Panovska A, Brezovska K, Grozdanova A, Apostolski S, ŠuturkovaLj. Optimization of ELISA method for determina-tion of serum anti-GM1 antibodies. Maced Pharm Bull 2011; 57: 318−20.
Perić S, Lavrnić S, Basta I, Damjanović D, Stosić-Opinćal T, Lavrnić D. Significance of magnetic resonance imaging in differential diagnosis of nontraumatic brachial plexopathy. Vojnosanit Pregl 2011; 68(4): 327−31.
Van Asseldonk JH, Franssen H, Van Berg-Vos RM, Wokke JH, Van Berg LH. Multifocal motor neuropathy. Lancet Neurol 2005; 4(5): 309−19.
Bouche P, Moulonguet A, Younes-Chennoufi AB, Adams D, Baumann N, Meininger V, et al. Multifocal motor neuropathy with con-duction block: a study of 24 patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psy-chiatr 1995; 59(1): 38−44.
Nguyen TP, Chaudhry V. Multifocal motor neuropathy. Neurol India 2011; 59(5): 700−6.
Katz JS, Saperstein DS. Asymmetric Acquired Demyelinating Polyneuropathies: MMN and MADSAM. Curr Treat Options Neurol 2001; 3(2): 119−25.
Azulay JP, Blin O, Pouget J, Boucraut J, Billé-Turc F, Carles G, et al. Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in patients with motor neuron syndromes associated with anti-GM1 antibodies: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Neurology 1994; 44(3 Pt 1): 429−32.
O'Ferrall EK, White CM, Zochodne DW. Demyelinating symme-tric motor polyneuropathy with high titers of anti-GM1 anti-bodies. Muscle Nerve 2010; 42(4): 604−8.
Kuwabara S, Cappelen-Smith C, Lin CS, Mogyoros I, Bostock H, Burke D. Excitability properties of median and peroneal motor axons. Muscle Nerve 2000; 23(9): 1365−73.
Burke D, Kiernan MC, Bostock H. Excitability of human axons. Clinical neurophysiology 2001; 112(9): 1575−85.
Van Berg-Vos RM, Franssen H, Wokke JH, Van Es HW, Van Berg LH. Multifocal motor neuropathy: diagnostic criteria that predict the response to immunoglobulin treatment. Ann Neu-rol 2000; 48(6): 919−26.
Katz JS, Barohn RJ, Kojan S, Wolfe GI, Nations SP, Saperstein DS, et al. Axonal multifocal motor neuropathy without conduction block or other features of demyelination. Neurology 2002; 58(4): 615−20.
Van Es HW. MRI of the brachial plexus. Eur Radiol 2001; 11(2): 325−36.
Wittenberg K, Adkins MC. MR imaging of nontraumatic brachial plexopathies: frequency and spectrum of findings. Radiographics 2000; 20(4): 1023−32.